monocot vs dicot Flashcards and Study Sets Quizlet Jun 20, 2017В В· Difference between monocot vs dicot Angiosperms are plants that have flowers and seeds encased in fruit. Angiosperms can be divided into to major categories, monocots and dicots. Monocots have one
Monocots vs Dicots What You Need To Know
Difference between Dicot Root and Monocot Root Plants. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between Dicot Root and Monocot Root. Difference # Dicot Root: 1. Cortex is comparatively narrow. 2. The epiblema, the cortex and even the endodermis are peeled off and replaced by cork., PDF Monocot and dicot plants contain stomata in their leaves as well as in their stem. 10/24/2017 Difference Between Stomata of Monocot and Dicot Root xylem was more susceptible to.
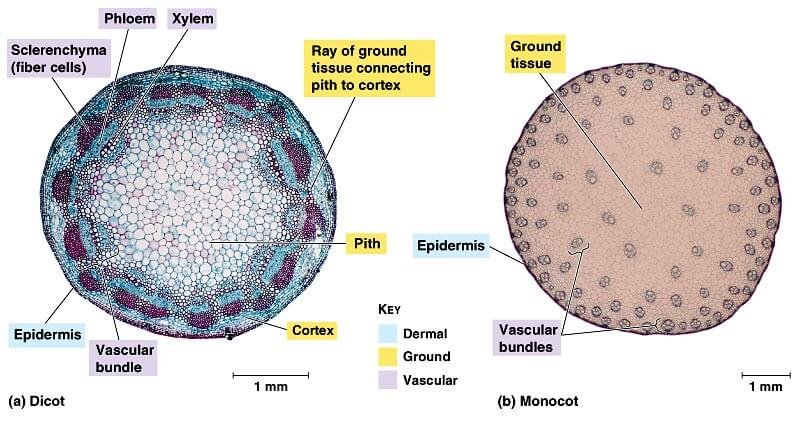
Monocots: More on Morphology. Monocots differ from other flowering plants in a number of features. Almost every basic botany course includes a unit in which dicot and monocot characters are compared. Monocot vs. Dicot. The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants' veins on leaves. However, there are many different things that separate monocots from dicots. In fact, monocots differ from dicots in four structural features: their …
It must be pointed out, however, that there are many exceptions to these characters in both groups, and that no single character in the list below will infallibly identify a flowering plant as a monocot or dicot. The table summarizes the major morphological differences between monocots and dicots; each character is dicussed in more detail below. Jul 02, 2018В В· Monocot root 1. Pericycle has lateral roots. 2. Number of xylem phloem elements are 8 to many. 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue are mostly sclerenchymatous. 5. Pith is large and well developed. 6. No secondary growth. 7....
It must be pointed out, however, that there are many exceptions to these characters in both groups, and that no single character in the list below will infallibly identify a flowering plant as a monocot or dicot. The table summarizes the major morphological differences between monocots and dicots; each character is dicussed in more detail below. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between Dicot Root and Monocot Root. Difference # Dicot Root: 1. Cortex is comparatively narrow. 2. The epiblema, the cortex and even the endodermis are peeled off and replaced by cork.
Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world. Jul 02, 2018В В· Monocot root 1. Pericycle has lateral roots. 2. Number of xylem phloem elements are 8 to many. 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue are mostly sclerenchymatous. 5. Pith is large and well developed. 6. No secondary growth. 7....
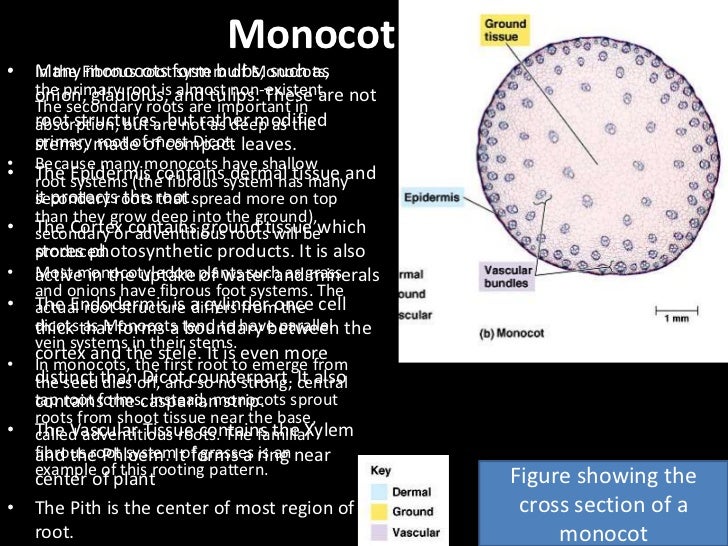
Objective. Our objective is to study the external features of Monocot and Dicot plants. The Theory. Flowering plants, also known as Angiosperms, are the most diverse group of land plants in the world, with at least 2,60,000 living species classified into 453 families. (The word Angiosperm finds its origin from two Greek words – вЂangio’ meaning covered and вЂsperma’ meaning seed. The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section (T.S.) taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass, bamboo, maize, Asparagus etc. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that, here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into Cortex and Endodermis.
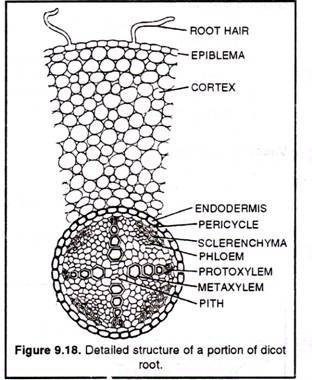
Dicot/Monocot Root Anatomy The figure shown below is a cross section of the herbaceous dicot root Ranunculus. The vascular tissue is in the very center of the root. The ground tissue surrounding the vascular cylinder is the cortex. An epidermis surrounds the entire root. The central region of vascular tissue is termed the Chapter 5 The Shoot System I: The Stem THE ECONOMIC VALUE OF WOODY STEMS THE FUNCTIONS AND ORGANIZATION OF THE SHOOT SYSTEM PRIMARY GROWTH AND STEM ANATOMY Primary Tissues of Dicot Stems Develop from the Primary Meristems The Distribution of the Primary Vascular Bundles Depends on the Position of Leaves Primary Growth Differs in Monocot and
PDF Monocot and dicot plants contain stomata in their leaves as well as in their stem. 10/24/2017 Difference Between Stomata of Monocot and Dicot Root xylem was more susceptible to Mar 02, 2019 · In the following quiz we’re going to be looking at monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Monocots are flowering plants whose seeds usually only contain one embryonic leaf, hence the name. In a similar vein, dicotyledons only possess seeds with two embryonic leaves, or cotyledons. Don’t worry, you don’t need to answer many questions, all we need is for you to identify monocots and dicots based
It must be pointed out, however, that there are many exceptions to these characters in both groups, and that no single character in the list below will infallibly identify a flowering plant as a monocot or dicot. The table summarizes the major morphological differences between monocots and dicots; each character is dicussed in more detail below. Bring your downloaded image pdf file to lab. 4. Bring personal protective gear (lab coat, goggles, gloves) to lab. 5. Bring to class four plants (two monocot species and two dicot Cross-section of a typical herbaceous monocot root (left) and a dicot root (right). Note that most dicot roots lack a pith and have a solid core of vascular tissue.
Bring your downloaded image pdf file to lab. 4. Bring personal protective gear (lab coat, goggles, gloves) to lab. 5. Bring to class four plants (two monocot species and two dicot Cross-section of a typical herbaceous monocot root (left) and a dicot root (right). Note that most dicot roots lack a pith and have a solid core of vascular tissue. Monocot vs Dicot Roots Lab Name_____ Analysis questions 1. Explain how the center of a monocot root differs from the center of a dicot root? 2. What is the function of the Xylem? 3. What is the function of the Phloem? 4. What is the purpose of the endodermis? 5. Where do lateral (secondary) roots arise? 6.
Learn monocot vs dicot with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of monocot vs dicot flashcards on Quizlet. Log in Sign up. monocot vs dicot Flashcards. monocot- fibrous root... dicot- tap root. seeds. monocot- 1 cotyledon... dicot- 2 cotelydons. flowers. To study the structural details of the stem or root of a monocot or dicot plant, it is essential to be familiarized with the sectioning and staining techniques used with plant materials. It is also necessary to take the sections with uniform thickness so that the light passes through them equally and the different tissues found in the material
Sep 14, 2012 · Roots: Fibrous vs. taproot. Once the embryo begins to grow its roots, another structural difference occurs. Monocots tend to have “fibrous roots” that web off in many directions. These fibrous roots occupy the upper level of the soil in comparison to … Conclusion. Monocot and Dicot are two terms which are very common when it comes to studying about plants. But there are many ways in which the main differences between them can be explained to the people who want to know more about them and that is what this article has done, given people a general idea about the differences between the two terms.
Monocot vs Dicot Roots Lab Name Botany. Monocot Root * Presence of thin walled cells in the epiblema. * Absence of cuticle and stomata. * Presence of unicellular root hairs. Pith is absent in dicot root; it is present in monocot, Chapter 5 The Shoot System I: The Stem THE ECONOMIC VALUE OF WOODY STEMS THE FUNCTIONS AND ORGANIZATION OF THE SHOOT SYSTEM PRIMARY GROWTH AND STEM ANATOMY Primary Tissues of Dicot Stems Develop from the Primary Meristems The Distribution of the Primary Vascular Bundles Depends on the Position of Leaves Primary Growth Differs in Monocot and.
Difference Between Monocot and Dicot Roots Compare the
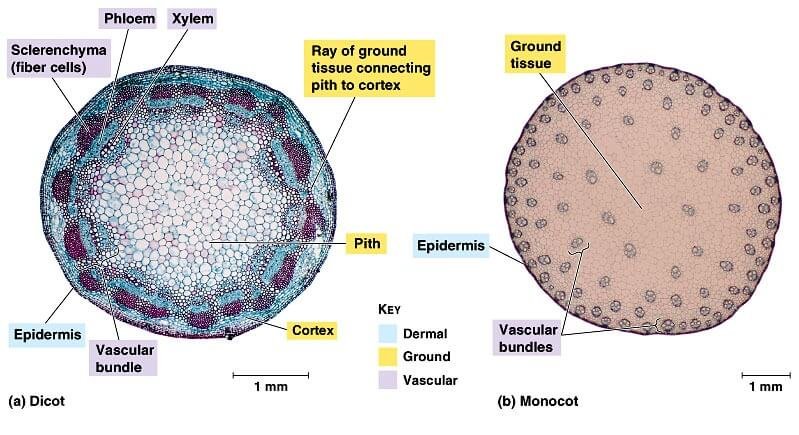
More on Morphology of the Monocots. Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world., Learn monocot vs dicot with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of monocot vs dicot flashcards on Quizlet. Log in Sign up. monocot vs dicot Flashcards. monocot- fibrous root... dicot- tap root. seeds. monocot- 1 cotyledon... dicot- 2 cotelydons. flowers..
lab3 plant structure Windward Community College. Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world., Objective. Our objective is to study the external features of Monocot and Dicot plants. The Theory. Flowering plants, also known as Angiosperms, are the most diverse group of land plants in the world, with at least 2,60,000 living species classified into 453 families. (The word Angiosperm finds its origin from two Greek words – вЂangio’ meaning covered and вЂsperma’ meaning seed..
Chapter 5 The Shoot System I The Stem

Monocot vs Dicot Roots Lab Name Botany. Monocot vs. Dicot. The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants' veins on leaves. However, there are many different things that separate monocots from dicots. In fact, monocots differ from dicots in four structural features: their … https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monocot May 02, 2017 · Main Difference – Monocot vs Dicot. Monocot and dicot are the two lineages of plants found in angiosperms. Angiosperms are flowering plants. They are the most successful, dominant as well as the diversified plants on earth. Over 250,000 species of herbs, shrubs and woody plants are found in ….

Aug 10, 2012В В· Monocot vs Dicot Roots . Root is one of the significant structures of a sporophyte of a vascular plant. It is the underground part of a plant, which has an important role in plant life. Absorbing nutrients, anchoring to the soil or another plant surface (i.e. epiphytes), storing of foods are some of the main functions of a root. Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem. Dicot stem vs Monocot stem. Dicot Stem. 1. Single layered epidermis with thick cuticle 2. Multicellular epidermal hairs may or may not be present 3. Hypodermis is generally collenchymatous 4. The different tissues are arranged in concentric fashion 5. Ground tissue is differentiated into hypodermis
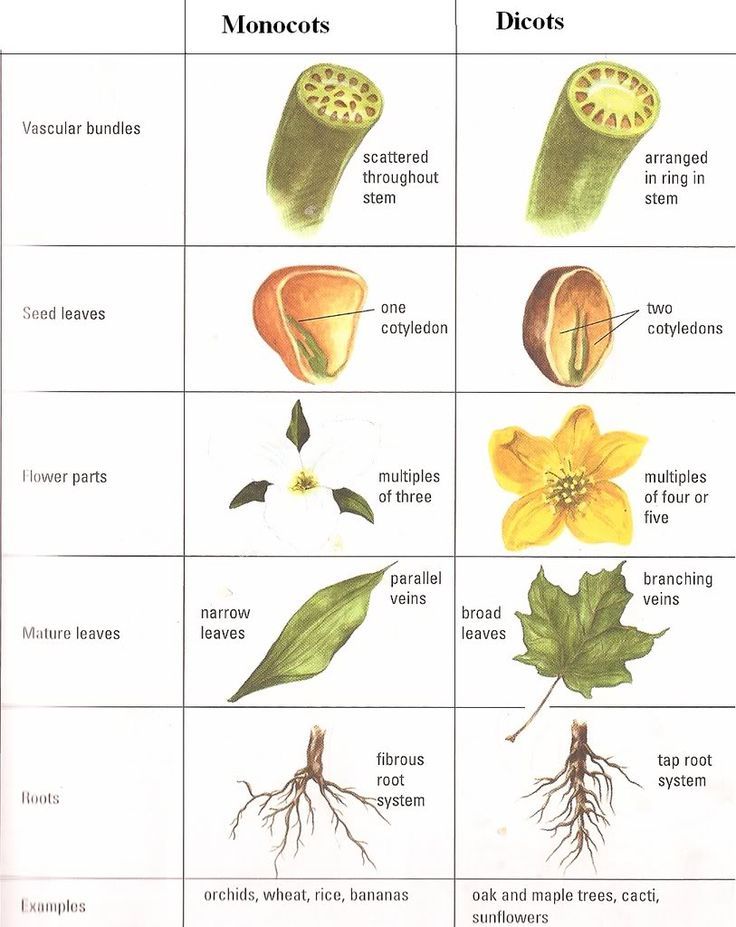
Monocot and Dicot characteristics Angiosperms are split into two groups: Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons The characteristics of each group are listed below. Monocots one cotyledon (seed leaf) two cotyledons (seed leaves) parallel veins netted veins scattered vascular bundles vascular bundles in a ring cross section of dicot stem under a Jun 20, 2017В В· Difference between monocot vs dicot Angiosperms are plants that have flowers and seeds encased in fruit. Angiosperms can be divided into to major categories, monocots and dicots. Monocots have one
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot roots. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots 2. Anatomy of Monocot Root. Monocot and Dicot Roots: Type # 1. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots: I. Cicer- Root: ADVERTISEMENTS: It is circular in outline (Fig. 170) and reveals following tissues from outside … Learn monocot vs dicot with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of monocot vs dicot flashcards on Quizlet. Log in Sign up. monocot vs dicot Flashcards. monocot- fibrous root... dicot- tap root. seeds. monocot- 1 cotyledon... dicot- 2 cotelydons. flowers.
Mar 02, 2019 · In the following quiz we’re going to be looking at monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Monocots are flowering plants whose seeds usually only contain one embryonic leaf, hence the name. In a similar vein, dicotyledons only possess seeds with two embryonic leaves, or cotyledons. Don’t worry, you don’t need to answer many questions, all we need is for you to identify monocots and dicots based ADVERTISEMENTS: Cortex is comparatively narrow. Related posts: Notes on the Internal Structure of Root Differences between Dicot Steams and Monocot Stems What is the difference between Dicot Stem and Dicot Root ? What is the difference between Vascular Bundles in Monocot and Dicot Stem What is the difference between Dicot Stem Anatomy and Monocot Stem …
Objective. Our objective is to study the external features of Monocot and Dicot plants. The Theory. Flowering plants, also known as Angiosperms, are the most diverse group of land plants in the world, with at least 2,60,000 living species classified into 453 families. (The word Angiosperm finds its origin from two Greek words – вЂangio’ meaning covered and вЂsperma’ meaning seed. Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem. Dicot stem vs Monocot stem. Dicot Stem. 1. Single layered epidermis with thick cuticle 2. Multicellular epidermal hairs may or may not be present 3. Hypodermis is generally collenchymatous 4. The different tissues are arranged in concentric fashion 5. Ground tissue is differentiated into hypodermis
Dicot/Monocot Root Anatomy The figure shown below is a cross section of the herbaceous dicot root Ranunculus. The vascular tissue is in the very center of the root. The ground tissue surrounding the vascular cylinder is the cortex. An epidermis surrounds the entire root. The central region of vascular tissue is termed the Root pattern. Monocot – It has fibrous roots. The roots are short and stingy. Dicot – It has a taproot system. The roots are long with a smaller roots growing from the original roots. (5, 6) Secondary growth. Monocot – None; Dicot – Yes; Stem and vascular system. Picture 5: The image shows the difference between monocot and dicot stem.
Monocot roots, interestingly, have their vascular bundles arranged in a ring. Dicot roots have their xylem in the center of the root and phloem outside the xylem. A carrot is an example of a dicot root. Diagram illustrating the tissue layers and their organization within monocot and dicot roots. Also, read Anatomy of Monocot and Dicot Plants. Monocot Root. These plant roots have a comparatively wider, and fibrous root-like structure. Dicot Root. These plant roots have a comparatively narrow, and tap root-like structure. Normally, dicots and monocots differ in four aspects which include stems, flowers, leaves, and roots.
dicot plant the phloem and the xylem are concentric rings on either side of the cambium (not always, but generally speaking). The cork cambium is the layer that produces the bark on the outside of the stem in dicots. Monocots are never woody, but they can still be very strong and sturdy. Look at figures XX and XX of monocot stems. Monocot vs. Dicot. The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants' veins on leaves. However, there are many different things that separate monocots from dicots. In fact, monocots differ from dicots in four structural features: their …
MONOCOT VS DICOT Classes of Plants Two classes : Angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperm = flowering plants Gymnosperms = non flowering plants (usually involves reproduction through seeds) Monocot vs. Dicot Angiosperms (flowering plants) are divided into monocots and dicots As the zygote grows into the embryo, the first leaves of the young plant develop and are called cotyledons (seed … Aug 10, 2012 · Monocot vs Dicot Roots . Root is one of the significant structures of a sporophyte of a vascular plant. It is the underground part of a plant, which has an important role in plant life. Absorbing nutrients, anchoring to the soil or another plant surface (i.e. epiphytes), storing of foods are some of the main functions of a root.
Conclusion. Monocot and Dicot are two terms which are very common when it comes to studying about plants. But there are many ways in which the main differences between them can be explained to the people who want to know more about them and that is what this article has done, given people a general idea about the differences between the two terms. Feb 23, 2015В В· What is the difference between Monocot and Dicot? there are other clues which tell you whether a plant is a monocot or a dicot, which is useful if you want to identify a plant that is mature and already flowering. which is provided in dicots by the woody stem and root. Monocots do not often grow into trees, because they do not have any
Jun 13, 2019В В· Both, Monocot and Dicot roots belong to plants. Monocots and Dicots differ from each other in four structures: leaves, stems, roots and flowers.The difference between dicot and monocot root is, dicot root contains xylem in the middle and phloem surrounding it. While, monocot root contain xylem and phloem in another manner, forming a circle. The monocot roots are fibrous while that of dicot are Start studying Monocot v. Dicot Worksheet. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. What is the root structure in monocot plants? Fiberous. What kind of root system do dicot plants have? Taproot.
Monocot v. Dicot Worksheet Flashcards Quizlet
Difference between Monocot and Dicot. May 02, 2017 · Main Difference – Monocot vs Dicot. Monocot and dicot are the two lineages of plants found in angiosperms. Angiosperms are flowering plants. They are the most successful, dominant as well as the diversified plants on earth. Over 250,000 species of herbs, shrubs and woody plants are found in …, May 02, 2017 · Main Difference – Monocot vs Dicot. Monocot and dicot are the two lineages of plants found in angiosperms. Angiosperms are flowering plants. They are the most successful, dominant as well as the diversified plants on earth. Over 250,000 species of herbs, shrubs and woody plants are found in ….
Monocot and Dicot Plants (Theory) Class 9 Biology
Internal Structure of Monocot Stem (Anatomy. May 02, 2017 · PDF by Lakna • 7 min read 0 Main Difference – Monocot vs Dicot Monocot and dicot are the two lineages of plants found in angiosperms. The main difference between monocot and dicot is, Jul 02, 2018 · Monocot root 1. Pericycle has lateral roots. 2. Number of xylem phloem elements are 8 to many. 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue are mostly sclerenchymatous. 5. Pith is large and well developed. 6. No secondary growth. 7.....
Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem. Dicot stem vs Monocot stem. Dicot Stem. 1. Single layered epidermis with thick cuticle 2. Multicellular epidermal hairs may or may not be present 3. Hypodermis is generally collenchymatous 4. The different tissues are arranged in concentric fashion 5. Ground tissue is differentiated into hypodermis Monocot Root * Presence of thin walled cells in the epiblema. * Absence of cuticle and stomata. * Presence of unicellular root hairs. Pith is absent in dicot root; it is present in monocot
The flowers of monocots and dicots differ in the number of petals they have. Monocots tend to have flower parts that occur in 3's ( 3, 6, 9, 12…). Dicot flowers usually have 4 to 5 petals. Color the monocot flower purple, and the dicot flower pink (make sure all petals are colored). MONOCOT VS DICOT Classes of Plants Two classes : Angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperm = flowering plants Gymnosperms = non flowering plants (usually involves reproduction through seeds) Monocot vs. Dicot Angiosperms (flowering plants) are divided into monocots and dicots As the zygote grows into the embryo, the first leaves of the young plant develop and are called cotyledons (seed …
Start studying Monocot v. Dicot Worksheet. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. What is the root structure in monocot plants? Fiberous. What kind of root system do dicot plants have? Taproot. Monocot and Dicot characteristics Angiosperms are split into two groups: Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons The characteristics of each group are listed below. Monocots one cotyledon (seed leaf) two cotyledons (seed leaves) parallel veins netted veins scattered vascular bundles vascular bundles in a ring cross section of dicot stem under a
Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world. Feb 15, 2014 · Difference between Dicot and Monocot 1. Difference between Monocot and Dicot The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. However, there are many different things that separate monocots from dicots.
It must be pointed out, however, that there are many exceptions to these characters in both groups, and that no single character in the list below will infallibly identify a flowering plant as a monocot or dicot. The table summarizes the major morphological differences between monocots and dicots; each character is dicussed in more detail below. Monocot Root * Presence of thin walled cells in the epiblema. * Absence of cuticle and stomata. * Presence of unicellular root hairs. Pith is absent in dicot root; it is present in monocot
The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section (T.S.) taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass, bamboo, maize, Asparagus etc. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that, here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into Cortex and Endodermis. Also, read Anatomy of Monocot and Dicot Plants. Monocot Root. These plant roots have a comparatively wider, and fibrous root-like structure. Dicot Root. These plant roots have a comparatively narrow, and tap root-like structure. Normally, dicots and monocots differ in four aspects which include stems, flowers, leaves, and roots.
The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between Dicot Root and Monocot Root. Difference # Dicot Root: 1. Cortex is comparatively narrow. 2. The epiblema, the cortex and even the endodermis are peeled off and replaced by cork. Sep 14, 2012 · Roots: Fibrous vs. taproot. Once the embryo begins to grow its roots, another structural difference occurs. Monocots tend to have “fibrous roots” that web off in many directions. These fibrous roots occupy the upper level of the soil in comparison to …
What's the difference between Dicot and Monocot? Flowering plants are divided into monocots (or monocotyledons) and dicots (or dicotyledons). This comparison examines the morphological differences in the leaves, stems, flowers and fruits of monocots and dicots. Contents 1 History of... Feb 23, 2015В В· What is the difference between Monocot and Dicot? there are other clues which tell you whether a plant is a monocot or a dicot, which is useful if you want to identify a plant that is mature and already flowering. which is provided in dicots by the woody stem and root. Monocots do not often grow into trees, because they do not have any
Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem. Dicot stem vs Monocot stem. Dicot Stem. 1. Single layered epidermis with thick cuticle 2. Multicellular epidermal hairs may or may not be present 3. Hypodermis is generally collenchymatous 4. The different tissues are arranged in concentric fashion 5. Ground tissue is differentiated into hypodermis The classification of flowering plants has been made for a long time on the basis of number of cotyledons they possess, i.e., in the form monocot vs. dicot system of categorization. The categorization or classification of plants on this basis doesn’t have any fundamental concepts for support.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot roots. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots 2. Anatomy of Monocot Root. Monocot and Dicot Roots: Type # 1. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots: I. Cicer- Root: ADVERTISEMENTS: It is circular in outline (Fig. 170) and reveals following tissues from outside … Jun 13, 2019 · Both, Monocot and Dicot roots belong to plants. Monocots and Dicots differ from each other in four structures: leaves, stems, roots and flowers.The difference between dicot and monocot root is, dicot root contains xylem in the middle and phloem surrounding it. While, monocot root contain xylem and phloem in another manner, forming a circle. The monocot roots are fibrous while that of dicot are
Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem Major Differences
Monocot vs Dicot Roots Lab Name Botany. Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world., Conclusion. Monocot and Dicot are two terms which are very common when it comes to studying about plants. But there are many ways in which the main differences between them can be explained to the people who want to know more about them and that is what this article has done, given people a general idea about the differences between the two terms..
What is the anatomy differences between monocot and dicot
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants. What's the difference between Dicot and Monocot? Flowering plants are divided into monocots (or monocotyledons) and dicots (or dicotyledons). This comparison examines the morphological differences in the leaves, stems, flowers and fruits of monocots and dicots. Contents 1 History of... https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monocotyledon ADVERTISEMENTS: Cortex is comparatively narrow. Related posts: Notes on the Internal Structure of Root Differences between Dicot Steams and Monocot Stems What is the difference between Dicot Stem and Dicot Root ? What is the difference between Vascular Bundles in Monocot and Dicot Stem What is the difference between Dicot Stem Anatomy and Monocot Stem ….
Jul 02, 2018В В· Monocot root 1. Pericycle has lateral roots. 2. Number of xylem phloem elements are 8 to many. 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue are mostly sclerenchymatous. 5. Pith is large and well developed. 6. No secondary growth. 7.... Aug 10, 2012В В· Monocot vs Dicot Roots . Root is one of the significant structures of a sporophyte of a vascular plant. It is the underground part of a plant, which has an important role in plant life. Absorbing nutrients, anchoring to the soil or another plant surface (i.e. epiphytes), storing of foods are some of the main functions of a root.
PDF Monocot and dicot plants contain stomata in their leaves as well as in their stem. 10/24/2017 Difference Between Stomata of Monocot and Dicot Root xylem was more susceptible to ADVERTISEMENTS: Cortex is comparatively narrow. Related posts: Notes on the Internal Structure of Root Differences between Dicot Steams and Monocot Stems What is the difference between Dicot Stem and Dicot Root ? What is the difference between Vascular Bundles in Monocot and Dicot Stem What is the difference between Dicot Stem Anatomy and Monocot Stem …
Monocot root 1. Periycle produces only lateral roots 2. Number of Xylem and phloem numerous ( 8 to many) 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue mostly sclerenchymatous sometimes parenchymatous. Mar 02, 2016В В· Onion root tip cell division stages at different magnifications(X400,X675 & X1500) - Duration: 4:45. Curiosity based learning with Durbadal Goswami 11,093 views
The flowers of monocots and dicots differ in the number of petals they have. Monocots tend to have flower parts that occur in 3's ( 3, 6, 9, 12…). Dicot flowers usually have 4 to 5 petals. Color the monocot flower purple, and the dicot flower pink (make sure all petals are colored). The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section (T.S.) taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass, bamboo, maize, Asparagus etc. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that, here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into Cortex and Endodermis.
The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section (T.S.) taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass, bamboo, maize, Asparagus etc. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that, here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into Cortex and Endodermis. Feb 23, 2015В В· What is the difference between Monocot and Dicot? there are other clues which tell you whether a plant is a monocot or a dicot, which is useful if you want to identify a plant that is mature and already flowering. which is provided in dicots by the woody stem and root. Monocots do not often grow into trees, because they do not have any
Monocot Root * Presence of thin walled cells in the epiblema. * Absence of cuticle and stomata. * Presence of unicellular root hairs. Pith is absent in dicot root; it is present in monocot Feb 15, 2014 · Difference between Dicot and Monocot 1. Difference between Monocot and Dicot The big difference that most people note about monocots and dicots is the formation of the plants’ veins on leaves. However, there are many different things that separate monocots from dicots.
To study the structural details of the stem or root of a monocot or dicot plant, it is essential to be familiarized with the sectioning and staining techniques used with plant materials. It is also necessary to take the sections with uniform thickness so that the light passes through them equally and the different tissues found in the material Monocot vs. Dicot. How do you tell the difference between two plants? Do you compare the shapes of the leaf or the type of stem? What about the different colored flowers? The act of separating plants into different categories is called classification. Classification is used to identify and organize the different types of plants in the world.
MONOCOT VS DICOT Classes of Plants Two classes : Angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperm = flowering plants Gymnosperms = non flowering plants (usually involves reproduction through seeds) Monocot vs. Dicot Angiosperms (flowering plants) are divided into monocots and dicots As the zygote grows into the embryo, the first leaves of the young plant develop and are called cotyledons (seed … Dicot or Monocot? How to Tell the Difference Flowering plants are divided into two groups - monocots and dicots. the first root that emerged from the seed, which is known as the radicle. Monocots have a root monocot vs. dicot in any search engine and you will …
Mar 19, 2013 · What is the difference between Monocot and Dicot Roots? • Vascular bundles in dicot root vary from 2 – 4 and rarely 6, whereas that of monocot root are numerous (8 or more bundles). • In dicot root, cambium appears as secondary meristem at the time of secondary growth whereas, in monocot root, cambium is absent. Jun 20, 2017 · Difference between monocot vs dicot Angiosperms are plants that have flowers and seeds encased in fruit. Angiosperms can be divided into to major categories, monocots and dicots. Monocots have one
Monocot root 1. Periycle produces only lateral roots 2. Number of Xylem and phloem numerous ( 8 to many) 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue mostly sclerenchymatous sometimes parenchymatous. MONOCOT VS DICOT Classes of Plants Two classes : Angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperm = flowering plants Gymnosperms = non flowering plants (usually involves reproduction through seeds) Monocot vs. Dicot Angiosperms (flowering plants) are divided into monocots and dicots As the zygote grows into the embryo, the first leaves of the young plant develop and are called cotyledons (seed …
Jul 02, 2018В В· Monocot root 1. Pericycle has lateral roots. 2. Number of xylem phloem elements are 8 to many. 3. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded. 4. Conjunctive tissue are mostly sclerenchymatous. 5. Pith is large and well developed. 6. No secondary growth. 7.... PDF Monocot and dicot plants contain stomata in their leaves as well as in their stem. 10/24/2017 Difference Between Stomata of Monocot and Dicot Root xylem was more susceptible to